
Long-running statements likely indicate resource contention.

lock_table: the table that is locked, or the table that contains the locked rows.lock_type: the type of the lock: RECORD (row) or TABLE.Some important columns to pay attention to: Note: your user will need the PROCESS privilege to access information_schema.innodb_* tables, and to see threads for other users. ORDER BY trx.trx_wait_started IS NOT NULL INNER JOIN performance_schema.threads t ON t.thread_id = trx.trx_mysql_thread_id
INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_trx trx ON trx.trx_id = l.lock_trx_id , concat( 'CALL mysql.rds_kill(', t.processlist_id, ') ') AS rds_kill_command , concat( 'KILL ', t.processlist_id, ' ') AS kill_command , time_to_sec(timediff(now(), trx.trx_started)) AS trx_length_sec , CASE WHEN l.lock_mode = 'S' THEN 'SHARED' WHEN l.lock_mode = 'X' THEN 'EXCLUSIVE' WHEN l.lock_mode = 'IS' THEN 'INTENTION_SHARED' WHEN l.lock_mode = 'IX' THEN 'INTENTION_EXCLUSIVE' ELSE l.lock_mode END AS lock_mode Here is a query to see both requested locks and locks held by InnoDB transactions: - MySQL <8.0.1 (2017) SELECT l.lock_type WHERE table_type = 'BASE TABLE' AND table_schema NOT IN ( 'information_schema', 'performance_schema', 'mysql') You can see what engine each of your tables is using with this query: SELECT table_schema It's highly likely that you're using InnoDB as the engine for your tables as it has been the default since MySQL v5.5.5 (2010). This is not an exhaustive list, but it gives us enough information for the sections below. Metadata locks on objects (schemas, tables, triggers, etc.) limit what sessions can alter the metadata of the database object.
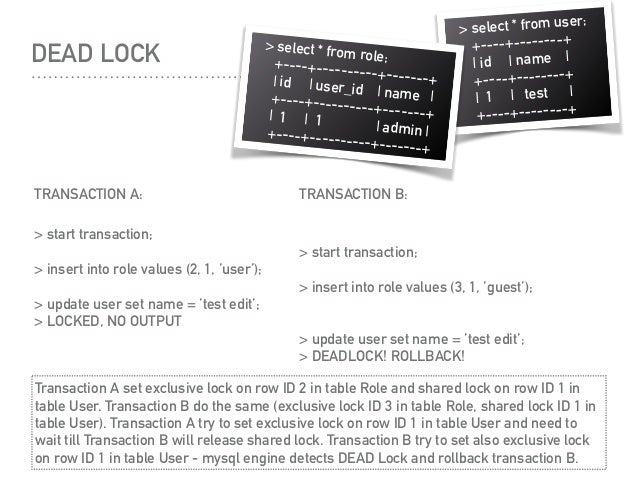
Mysql deadlock timeout update#
UPDATE or DELETE) has no suitable index, then InnoDB will obtain a write lock on every row in the table. That means a row write lock won't prevent row reads from other sessions. FROM statements do not need to obtain row read locks unless the transaction isolation level is set to SERIALIZABLE.

If a row has a write or an "exclusive" lock then only the session holding the lock can modify the row. If a row has a read or a "shared" lock then no session can modify the row until the lock is released, but any session can read the row. Row locks on individual rows limit what sessions can read or update those rows. Table locks on either base tables or views limit what sessions can read from or write to the table. MySQL (and most relational databases) have a few different types of locks to limit concurrent access from different sessions, protecting schema and data integrity. Poorly optimized queries and excessive connections can cause problems in MySQL, here's a quick way to identify and kill them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
